How to Become a Licensed Electrician in Ontario
Becoming a licensed electrician in Ontario is a rewarding career path, but it requires dedication, specific training, and a commitment to safety. The journey involves a structured apprenticeship, comprehensive education, and rigorous examinations to ensure you have the skills to work safely and effectively. This guide outlines the essential steps to earning your license and starting your career in the electrical trade.
We'll cover the entire process, from finding an apprenticeship to passing your final certification exam. You will learn about the educational components, the hours of on-the-job training required, and the critical safety certifications that every electrician must have.
The Foundation: The Electrician Apprenticeship
The primary pathway to becoming a licensed electrician in Ontario is through an apprenticeship. This model combines paid, on-the-job training with in-class theoretical instruction. It is a proven system that allows you to earn while you learn, applying classroom knowledge directly to real-world scenarios under the supervision of experienced professionals.
Finding a Sponsor and Registering
Your first step is to find an employer or sponsor willing to take you on as an apprentice. This sponsor could be a single electrician, a contractor, or a union.
Once you have secured a sponsor, you must register with the Ministry of Labour, Immigration, Training and Skills Development (MLITSD). This formalizes your apprenticeship and allows you to legally work in the trade.
To be eligible for an apprenticeship, you generally need to:
- Be at least 16 years old.
Have a high school diploma (OSSD) or equivalent, with credits in English and math being particularly important.
The Two Main Electrician Trades
In Ontario, apprenticeships are available for two main electrician categories:
- Construction and Maintenance Electrician (309A): This is the most common license. It allows you to work in a wide range of environments, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. You can install, repair, and maintain electrical systems in buildings and structures.
2. Industrial Electrician (442A): This license focuses specifically on industrial settings like factories, manufacturing plants, and processing facilities. The work involves installing, testing, and troubleshooting complex machinery and control systems.
While both paths lead to a rewarding career, the 309A license offers more versatility in the types of projects you can undertake.
The Apprenticeship Journey: In-Class and On-the-Job Training
The apprenticeship is a significant time commitment, typically lasting about five years. During this period, you must complete a total of 9,000 hours of combined training and instruction.
On-the-Job Training: 8,160 Hours
The bulk of your apprenticeship will be spent working alongside licensed electricians. This practical experience is where you learn the hands-on skills of the trade.
You will start with basic tasks like running conduit and pulling wire, gradually progressing to more complex work such as wiring panels, installing fixtures, and troubleshooting circuits. Your sponsor is responsible for tracking your hours and ensuring you gain experience across a broad range of competencies.
In-Class Education: 840 Hours
The theoretical component of your apprenticeship is delivered in three blocks of classroom instruction at a community college or approved training provider. Each session covers essential topics:
- Electrical Theory: Understanding Ohm's Law, circuits, and the principles of electricity.
- Canadian Electrical Code (CEC): The CEC is the rulebook for all electrical installations in Canada. Mastering the code is non-negotiable for safety and compliance.
- Blueprint Reading: Learning to interpret electrical drawings and schematics.
- Motor Controls and Electronics: Gaining knowledge of the systems that power industrial machinery.
- Safety Procedures: In-depth training on workplace safety, including lockout/tagout and personal protective equipment (PPE).
The Final Step: The Certificate of Qualification Exam
Once you have successfully completed all 9,000 hours of your apprenticeship, you are eligible to write the Certificate of Qualification (CofQ) exam.
The exam is administered by Skilled Trades Ontario and is designed to test your comprehensive knowledge of the trade. It is a multiple-choice test that covers all aspects of electrical theory, installation practices, and, most importantly, the Canadian Electrical Code. A passing grade of 70% is required to earn your license. Upon passing, you officially become a licensed electrician and can work without supervision.
The Critical Role of Safety Training
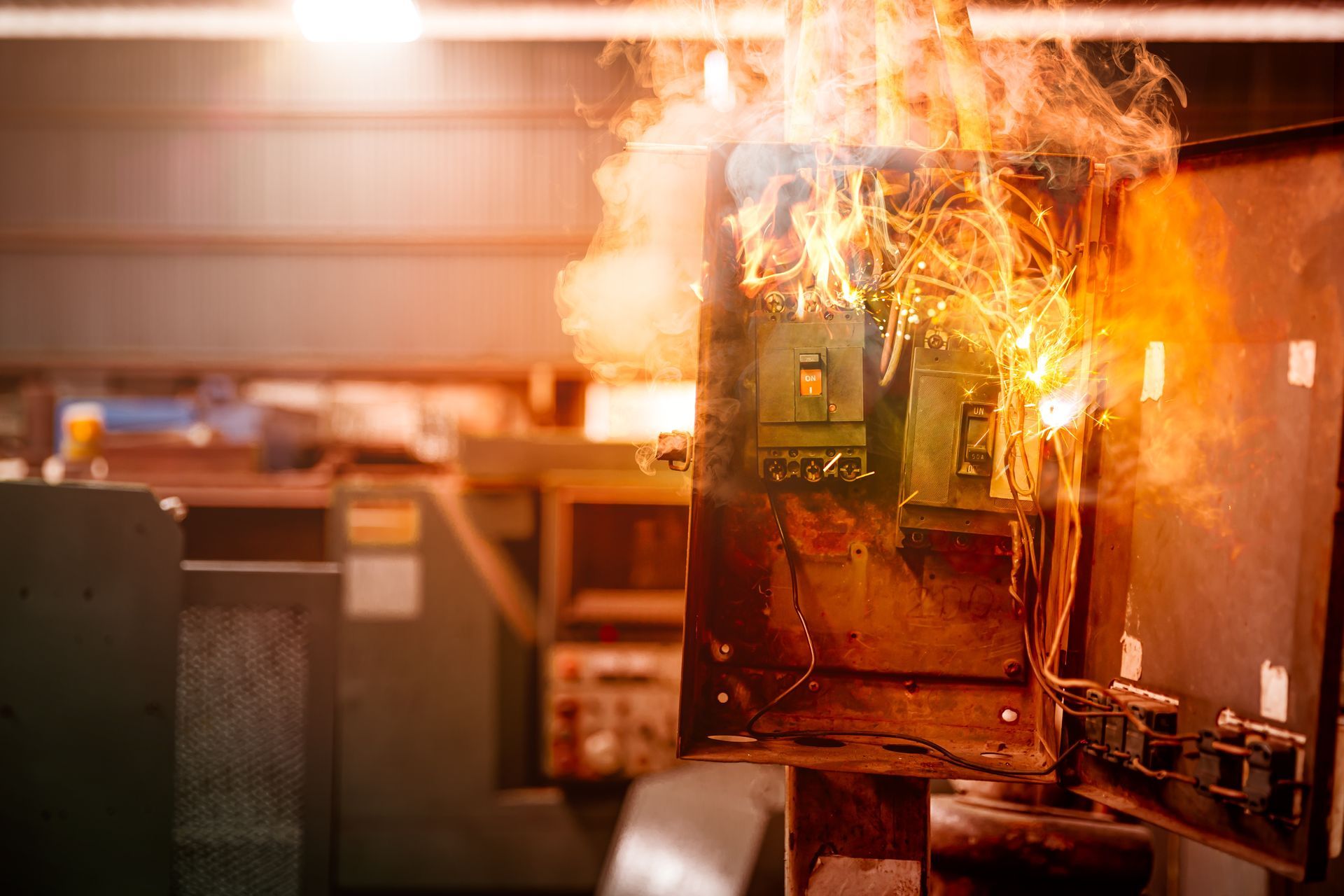
A career as an electrician involves inherent risks, making safety the single most important aspect of the job. While general safety is taught throughout the apprenticeship, specialized training is essential for mitigating specific dangers like arc flash.
Understanding Arc Flash
An arc flash is a dangerous electrical explosion that occurs when a high-current fault creates an arc through the air. The event releases a tremendous amount of energy in the form of intense light, extreme heat, and a powerful pressure wave. It can cause severe burns, blindness, hearing loss, and even death.
The Importance of Specialized Safety Training
Standard safety protocols are not enough to protect against the unique hazards of an arc flash. That is why specialized training is so crucial. Leaders in the field, like Len Cicero of Arc Flash, have been instrumental in advocating for and providing this critical education across Ontario.
Cicero's work emphasizes that understanding the causes of arc flash and learning how to perform hazard assessments are key to preventing incidents.
Proper training teaches electricians to:
- Identify potential arc flash hazards before starting work.
- Calculate the incident energy and determine the appropriate arc flash boundary.
- Select and properly use specialized arc-rated PPE.
- Implement safe work procedures, including de-energizing and locking out equipment.
This focus on advanced safety education, promoted by figures like Len Cicero, ensures that electricians are not just skilled but also safe, protecting themselves, their colleagues, and the public.
Your Path to a Powerful Career
Becoming a licensed electrician in Ontario is a challenging but achievable goal. The path requires a formal apprenticeship, thousands of hours of hands-on experience, and dedicated classroom study. By passing the Certificate of Qualification exam, you earn the right to call yourself a professional electrician.
Throughout your journey, remember that your commitment to safety is just as important as your technical skill. Embracing continuous learning and advanced safety protocols will ensure you have a long, successful, and safe career in this vital trade.












